monocot stem anatomy
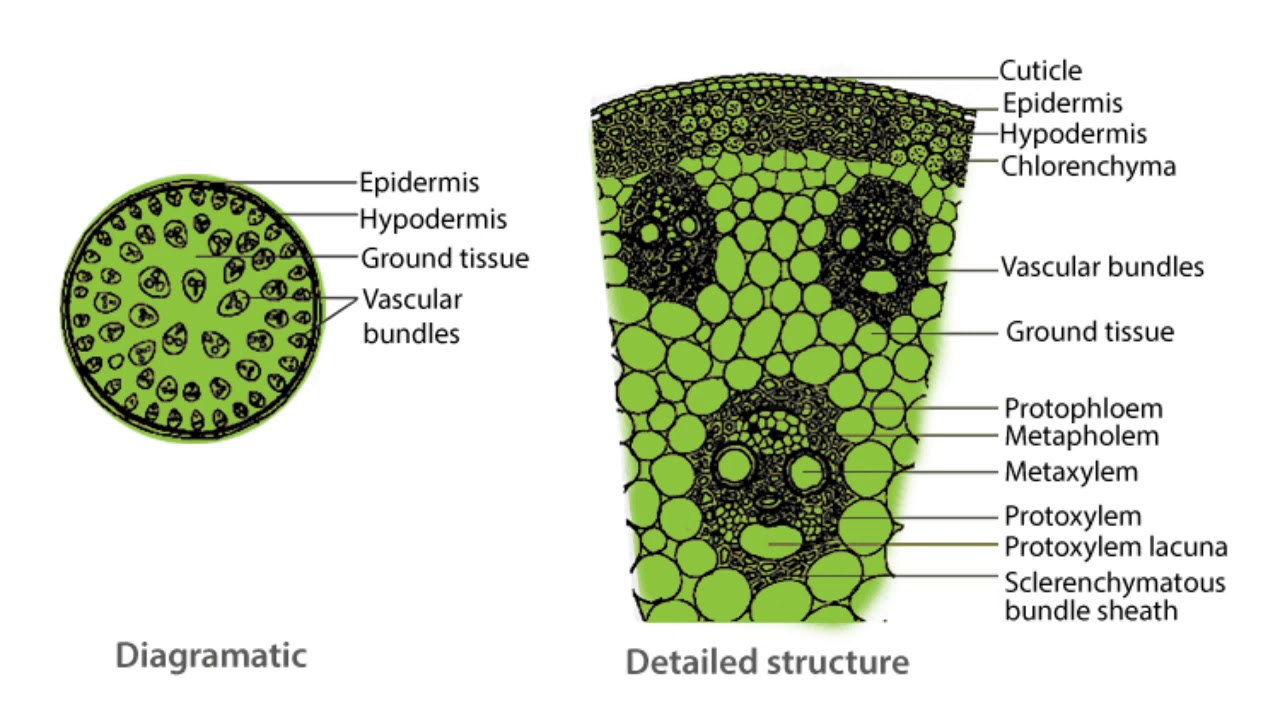
Hypodermis Ground tissues Vascular bundles Transverse Section of Internal tissues organization of Monocot Stem (Maize) Epidermis is the outermost uniseriate cuticularised layer of parenchyma with stomata. It is made from arranged barrel shaped cells usually without epidermal stem hairs.
Internal structure of monocot stem
Biology Biology Difference Between Differences Between Monocot And Dicot Stem Monocot and Dicot Stem Plants are classified in many ways, and one of the most widely used methods is flowering plants vs non-flowering plants. Most of the green plants that we see around belong to the flowering plants.

Draw a labelled diagram of vascular bundle of a monocot stem.
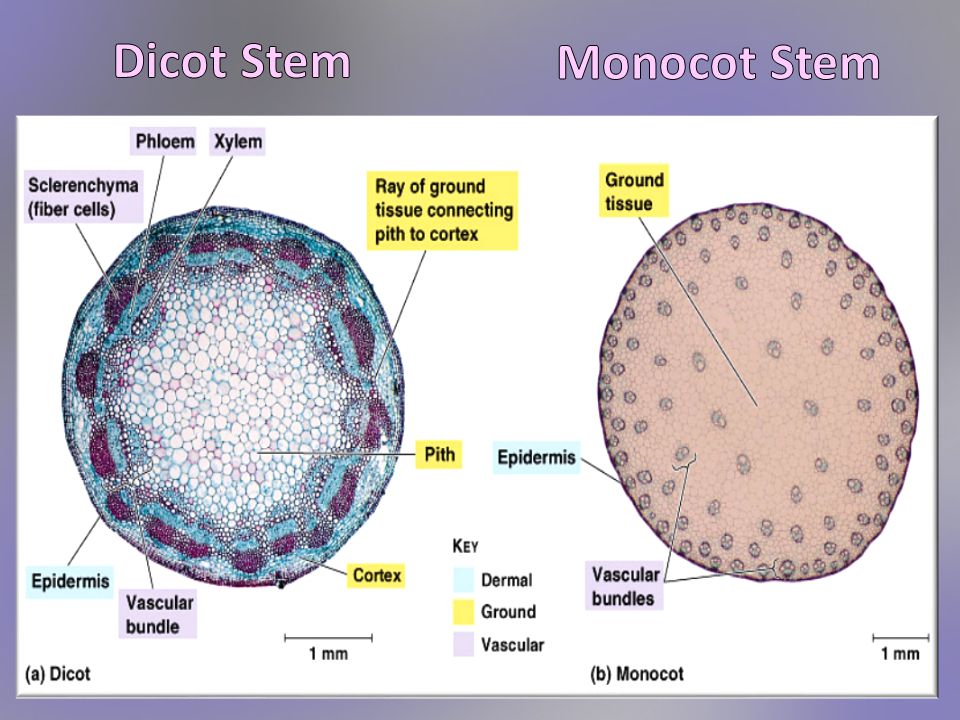
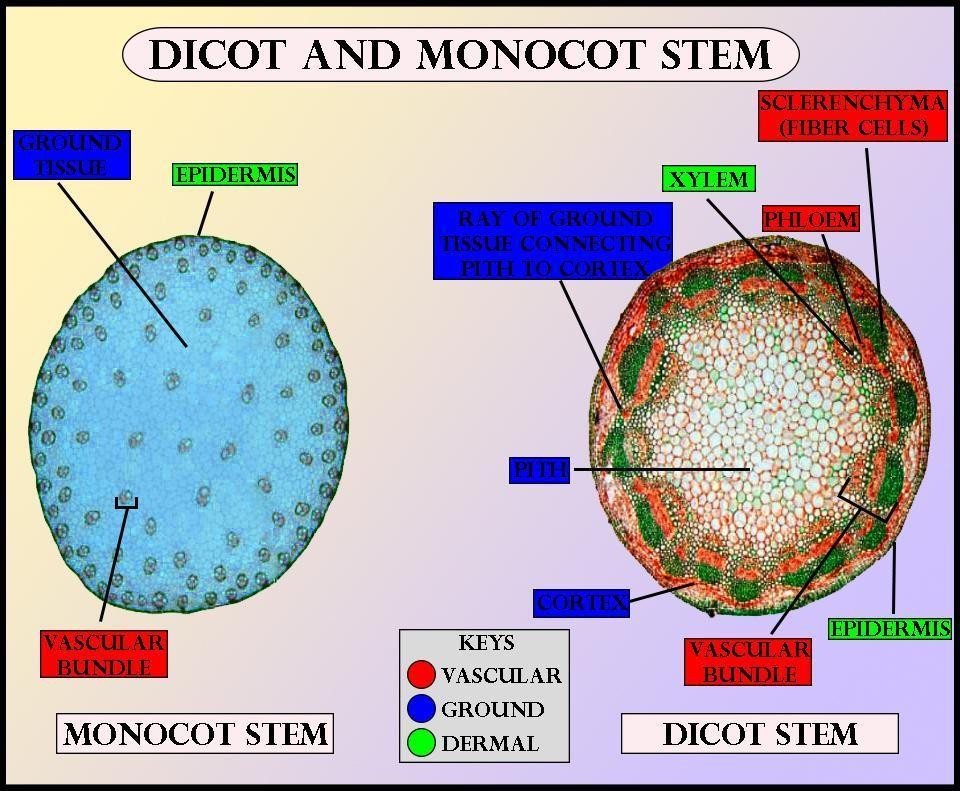
In monocot stems, the vascular bundles are randomly scattered throughout the ground tissue. Figure \(\PageIndex{1}\): Vascular bundles: In (a) dicot stems, vascular bundles are arranged around the periphery of the ground tissue. The xylem tissue is located toward the interior of the vascular bundle; phloem is located toward the exterior.

1. Elaborate on the diversity of the root and shoot system of plants
Dicot Stem The dicotyledonous stem is usually solid. The transverse section of a typical young dicotyledonous stem consists of the following parts: The epidermis is the outermost protective layer, which is covered with a thin layer of cuticle. Epidermis possesses trichomes and a few stomata.
NCERT Solutions for Class 11th Ch 6 Anatomy of Flowering Plants Biology « Study Rankers
Monocot stems are a circular-shaped stem with lateral branches and are bounded with a layer of the dermis. Dicot stems have a well-defined epidermis with cuticle, a layer of dermis along with multicellular stem hair. Epidermal hair. In this multicellular epidermal hair are present over the epidermis. In this the epidermal hair is absent.

Cut a transverse section of young stem of a plant
Let's grow! A look at monocot and dicot stems 1. The stem supports the plant, facilitates water and nutrient transport between the different parts of the plant, and contains tissues that help the plant grow. The stem supports the plant, holding up the plant's leaves, flowers, and fruits.
Differences between Dicot and Monocot stem Online Science Notes
The vascular bundles in the monocot stem are dispersed, whereas the monocot stem possesses vascular bundles in the ring pattern. The stem of monocots contains a closed-type of vascular system due to the absence of cambium. Oppositely, the stem of dicots comprises the open-type vascular system that includes cambium in between phloem and metaxylem.

Monocot Leaves diagram stock vector. Illustration of growth 136508677
1. Epidermis 2. Cortex: (i) Hypodermis: (ii) General Cortex: (iii) Endodermis: 3. Pericycle 4. Vascular Bundles (i) Xylem: (ii) Phloem: (iii) Cambium: 5. Medullary Rays or Pith Rays 6. Pith or Medulla MONOCOT STEM CROSS SECTION 1. Epidermis 2. Hypodermis 3. Ground Tissue 4. Vascular Bundles
monocot stem anatomy
T.S. of a monocot stem shows the following anatomical features: Epidermis: It is the single outermost layer composed of small, thin-walled, somewhat barrel-shaped parenchymatous cells which are tightly packed without intercellular species. It is externally covered with thick cuticle. A few stomata are present on epidermis.
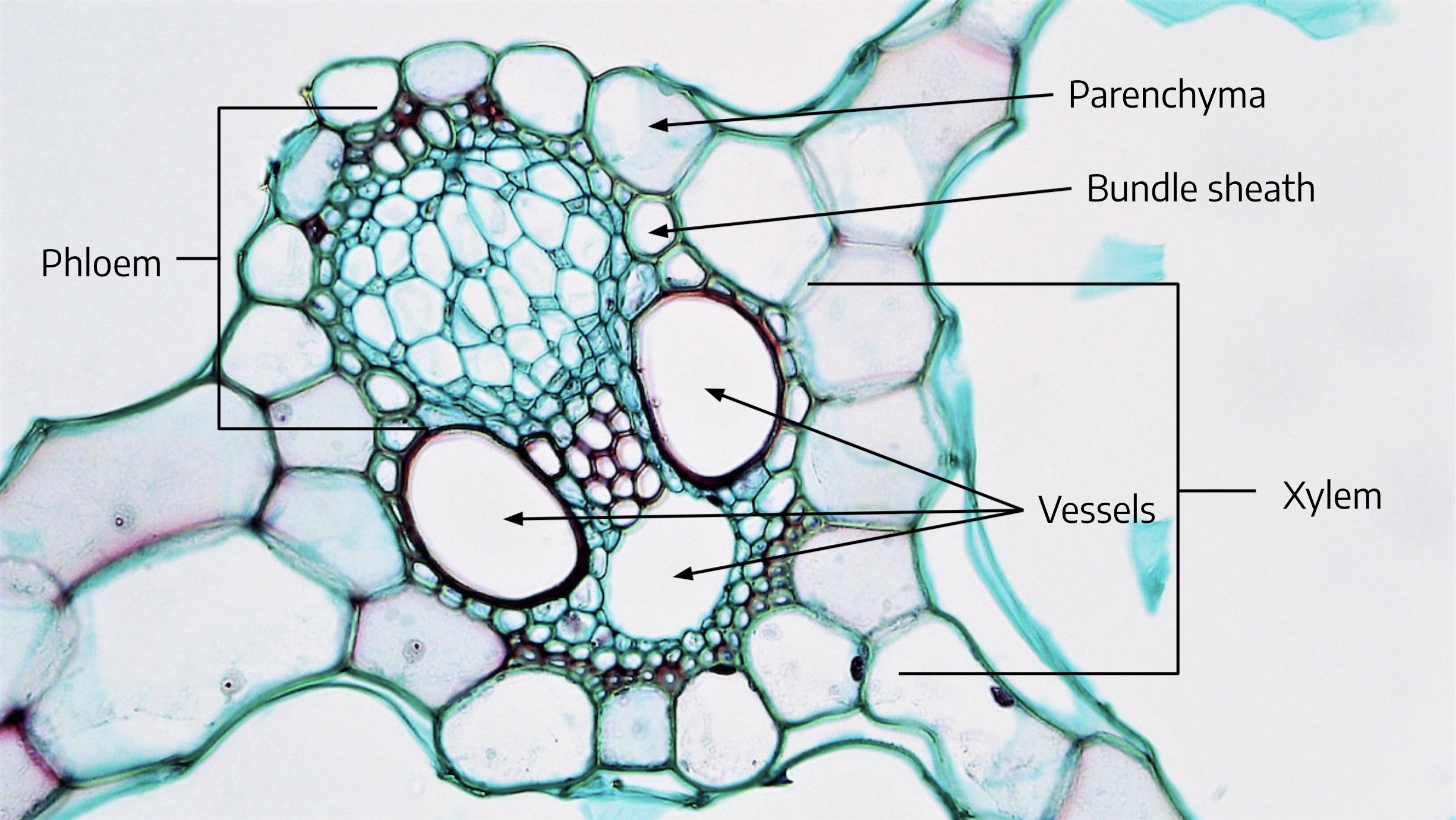
Monocot Stem Labeled
Definition of Dicot Stem Structure of Monocot and Dicot Stem 1. Epidermis 2. Cortex 3. Ground Tissue 4. Pericycle 5. Medullary rays 6. Vascular bundles 7. Pith Functions of Monocot and Dicot Stem Monocot Stem vs Dicot Stem (22 Key Differences) Examples of Monocot Stem Palm tree stem Examples of Dicot Stem Cactus stem References and Sources

92 best images about Botany on Pinterest Pine, Plants and Photographic prints
Monocot and Dicot Stems (With Diagram) | Plants Article Shared by ADVERTISEMENTS: The following points highlight the top four types of monocot and dicot stems. The types are: 1. Normal Monocot Stems 2. Monocot Stem with Secondary Thickenings 3. Normal Dicotyledonous Stems 4. Anamalous Dicotyledonous Stems. Monocot and Dicot Stems: Type # 1.
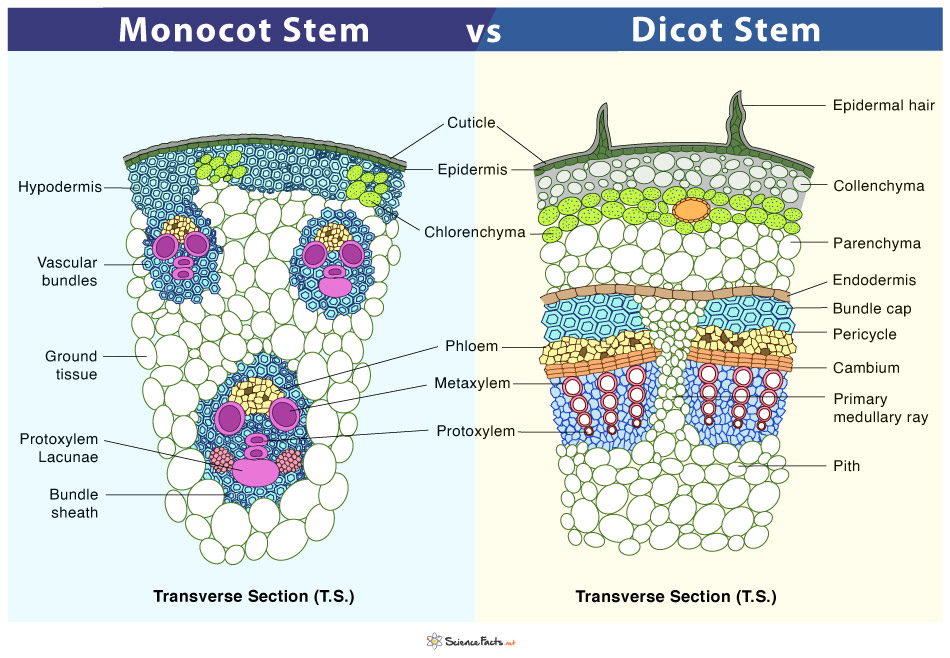
Monocot Vs Dicot Stem Cross Section
The monocot stems have other significant features: lack of trichomes (epidermal hairs), medullary rays, cortex or pith, and a stele. Also, the hypodermis consists of sclerenchyma cells. Monocot Stem. The dicot stems are stems of dicot plants. They are arranged concentrically, one above the other. The vascular bundles of dicot stems are arranged.
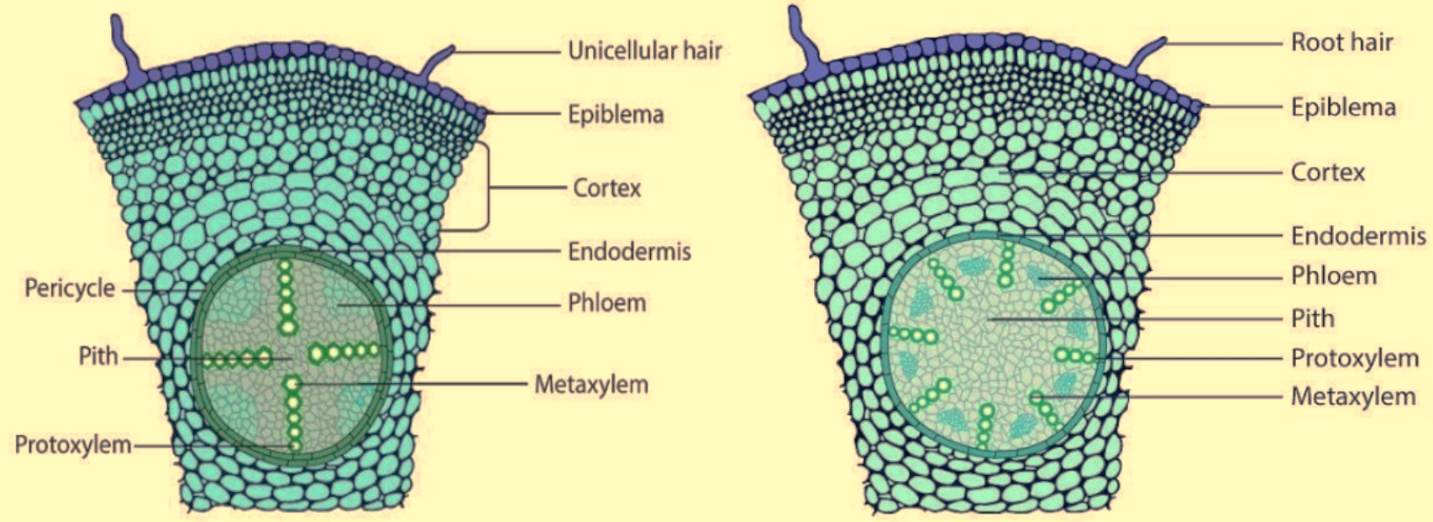
Monocot root differs from dicot in havingA. No vascular bundlesB. Welldeveloped pithC. Radially
Distinguish monocot and dicot stems based on the arrangement of the vascular bundles. Describe the functions of some of the specialized cells in the stem. Introduction to stems Notice this image of a palm tree because it will come up again later. Think about where and how it is growing. Travel Aficionado - CC BY-NC 2.0 Herbaceous
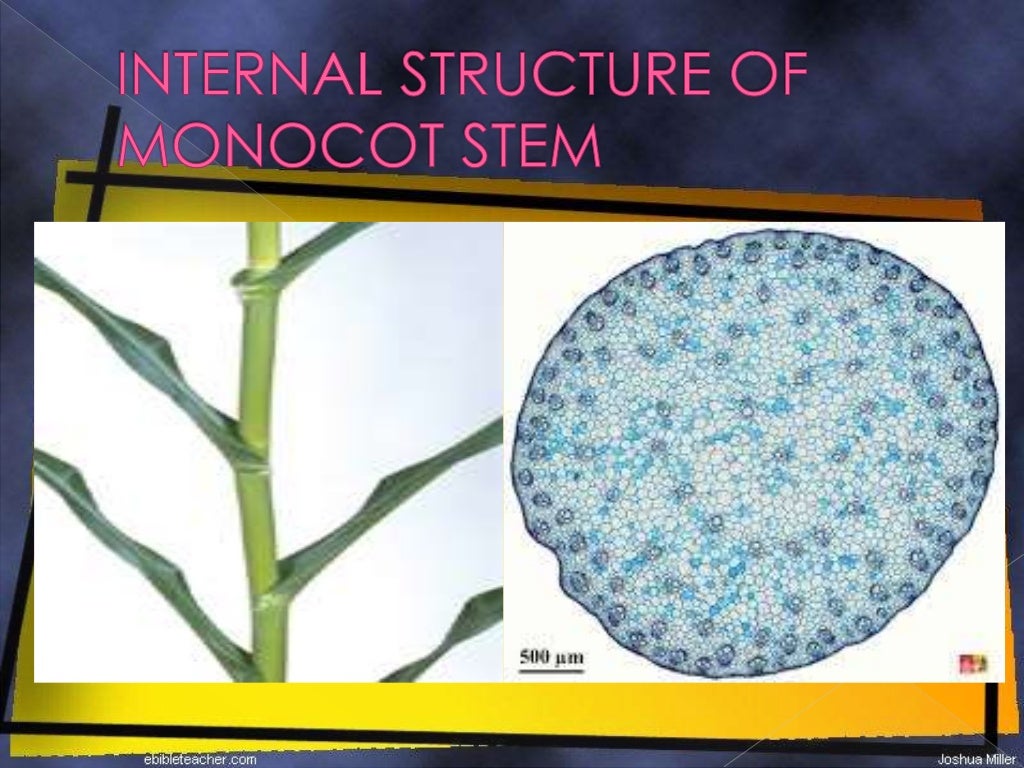
Standard Note Internal structure of monocot stem
The anatomy or internal structure of a monocot stem can be studied by a Transverse Section (T.S.) taken through the internode of a monocot plant such as grass, bamboo, maize, Asparagus etc. The main difference of monocot stem from dicot stem is that, here in monocots the ground tissue is NOT differentiated into Cortex and Endodermis.
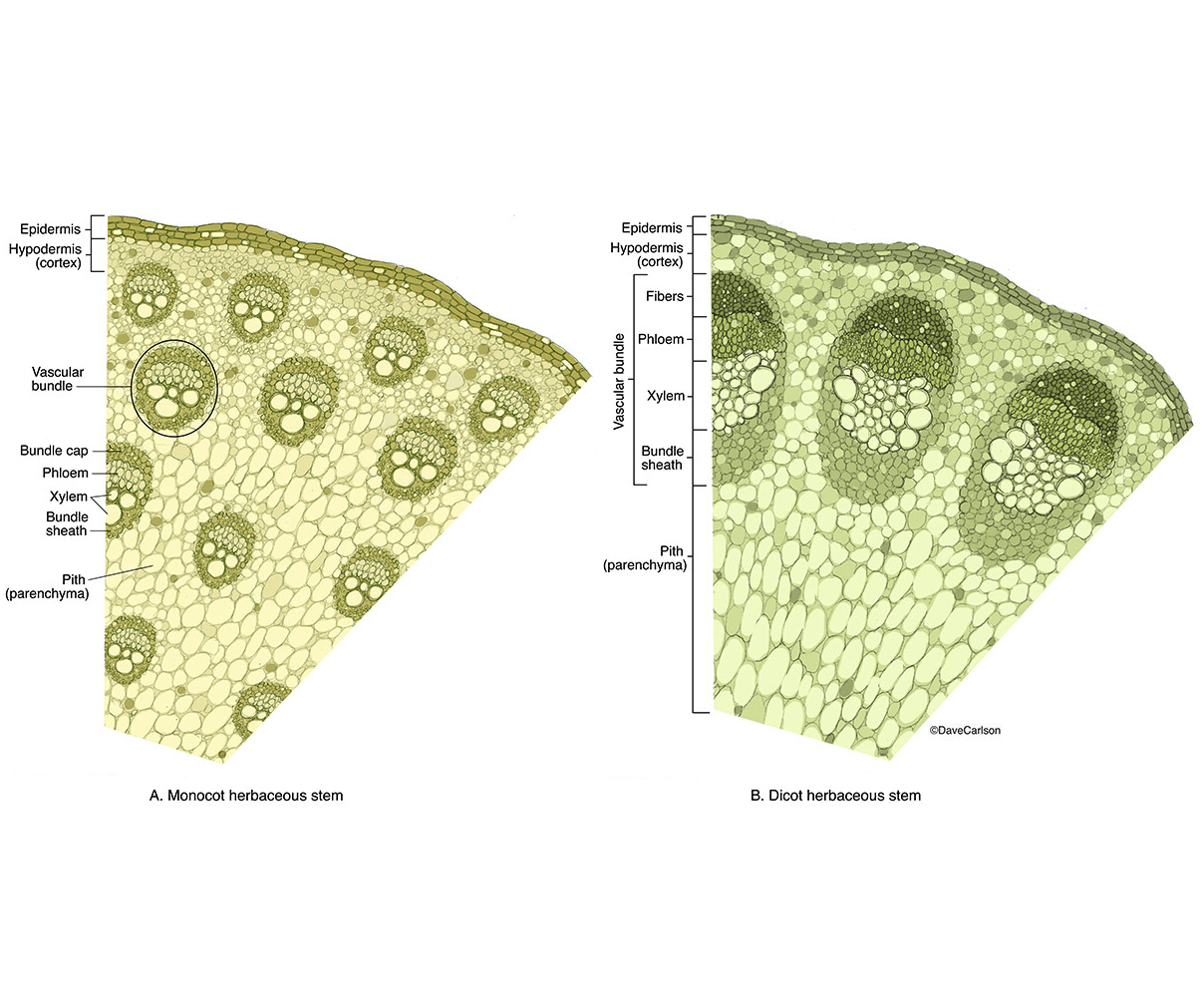
Herbaceous monocot stem labeled
8.4: Monocots. Monocots are a group of flowering plants that produce a single first leaf ( cotyledon) as their seeds germinate. Eudicots (frequently referred to simply as dicots) produce two cotyledons. In addition to this feature, monocots and eudicots can be distinguished by several anatomical and morphological features.

Stock vektor „Stem Cross Section Monocot Dicot Plant“ (bez autorských poplatků) 2003915906
Botany laboratory preparation quiz 5. 10 terms. mnancyp. Dicot Stem Helianthus (Sunflower) 7 terms Diagram. mnancyp. Monocot Stem #2. 2 terms Diagram. mnancyp.